Note to blog subscribers: Click on the Heading to view posts on the website with interactive course content, quizzes and updated materials.
Live Lecture
Session Outline
- A lot of familiar (or less familiar) words about numbers.
- Exploring their precise meaning.
- Building up for problems to come in upcoming sessions.
- Why?
- Questions may contain these words.
- Some minor questions we never asked
- Is 0 a Natural number?
- Is 19.333333… a rational number?
- Is π=22/7?
Interesting Sets of Numbers We Talked About
“Precise” Meanings
Natural Numbers: The counting numbers like 1, 2, 3, 4… are called natural numbers.
Whole numbers: Natural numbers along with zero are called whole numbers.
Integers: All counting numbers including zero and the negatives of the counting numbers form the set of integers. Hence …, –3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3… are all integers.A few terms to remember: “Positive Integers”, “Negative Integers”, “Non-negative integers” and “Non-positive integers”.
Classification of Integers: Even (divisible by 2), Odd (not divisible by 2).
Rational Numbers (Fractions): A rational number represents a part of a whole or, more generally, any number of equal parts.
Mixed Fraction: An improper fraction can be expressed as a whole number and a proper fraction. This expression is called a mixed fraction.
Decimal representation of rational numbers: When a rational number is written in decimal points, the digits after the decimal will
- Either stop after a while (Eg. 1.343443)
- Or repeat the same pattern forever (Eg. 1.546754675467…. “5467” repeats forever).
Irrationals: Numbers with infinite decimal expansion without any pattern are called irrationals. π is an irrational number.
Real numbers: Rational numbers, along with irrational numbers are called real numbers.
Quiz
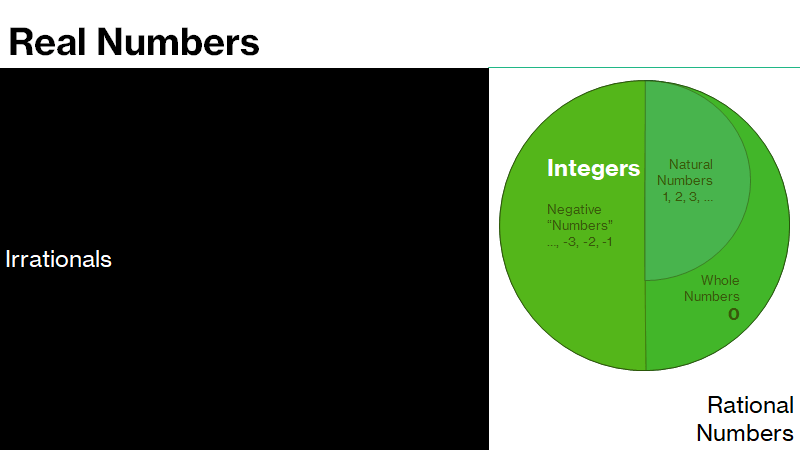
Additionally, we used terms like, “Sets”, “Venn Diagram”, “[set] contained in [another set]” etc.
Observations from Chair-Arranging Experiment
- Odd number of chairs cannot be arranged in two rows to make a perfect rectangle.
- Even number of chairs can be arranged in two rows to make a perfect rectangle.
- Addition
- Even + Even = Even
- Odd + Odd = Even
- Even + Odd = Odd
- Odd + Even = Odd
- Multiplication
- Even × Even = Even
- Even × Odd = Even
- Odd × Even = Even
- Odd × Odd = Odd
Classification of Natural Numbers
Prime Numbers: A natural number which has exactly two positive factors (divisors), namely itself and 1. For example, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, …
Composite Numbers: A natural number which has more than two positive factors. For example: 4, 6, 8, 9, 10,…
Note: 1 is neither prime nor composite as it has only one factor. Note the correction from how it was mentioned in the video lecture.
Quizzes
Here’s a cartoon to end it in a fun note:

More Materials
Follow us on one of these modes for more quizzes and updates. Feel free to ask your doubts in the comments below or in the video comments!
More materials and video descriptions will be given in this blog. Please don’t forget to follow this blog!
You can print this page for PDF.